As an analyst, you play a crucial role in solving crimes. Harnessing the power of graphs and the many features of GraphAware Hume can help stop criminals and bring justice to their victims. With the increasing advancements in technology, it is now easier than ever to track suspects and gather evidence that can aid in an investigation. One of the most powerful tools available to you is the capability of performing geospatial and temporal analysis.
Understanding Geospatial and Temporal Analytical Tools
Geospatial analysis is a potent feature within Hume that can be used to provide meaningful insight in the relationships between events, objects, and people in a given area within the knowledge graph. It can be used to identify hotspots of criminal activity and to map out crime patterns. It can also be used to identify links between crimes, helping to identify potential links between suspects. Additionally, geospatial analysis can be used to identify areas of high risk for crime and help to develop strategies to reduce these risks.
Temporal analysis allows for a more detailed view of crime over time. It can be used to identify trends in criminal activity, such as seasonal fluctuations or changes in the rate of crime. It can also be used to identify correlations between different types of crimes or between different kinds of suspects. Additionally, temporal analysis can be used to identify changes in the size or location of criminal activity, helping to better understand the dynamics of criminal activity in a given area.
When these two types of analysis are combined, they can provide a comprehensive view of a crime. By combining geospatial and temporal analysis, law enforcement can gain a broad and deep understanding of how a particular crime occurred, who was involved, and where and when it occurred. This information can be used to make informed decisions, develop strategies to reduce crime, and ultimately protect the communities you serve.
Case Background and Data Collection
Using geospatial and temporal analytical tools Hume can streamline the process of identifying patterns and connections between individuals and events. Imagine a real-world scenario in which a string of retail burglaries has occurred in a busy shopping district. The police have gathered CCTV footage from the scene but have no clear suspects. Using Hume, analysts easily create a single view of intelligence that includes information about the burglaries, including time, location, and method of entry. They can also include information about individuals who have been seen in the area around the time of the burglaries.
Data Analysis and Visualisation
With this information, intelligence analysts can use Hume’s geospatial and temporal analysis capabilities to identify patterns and connections that may not be immediately apparent. For example, they can utilise collected mobile phone GPS data to ascertain when and where specific individuals crossed paths, met or appeared near the crime scene of each burglary or other location of interest. They can also use Hume’s graph visualisation tools to map out the connections between these individuals and other events or people of interest.
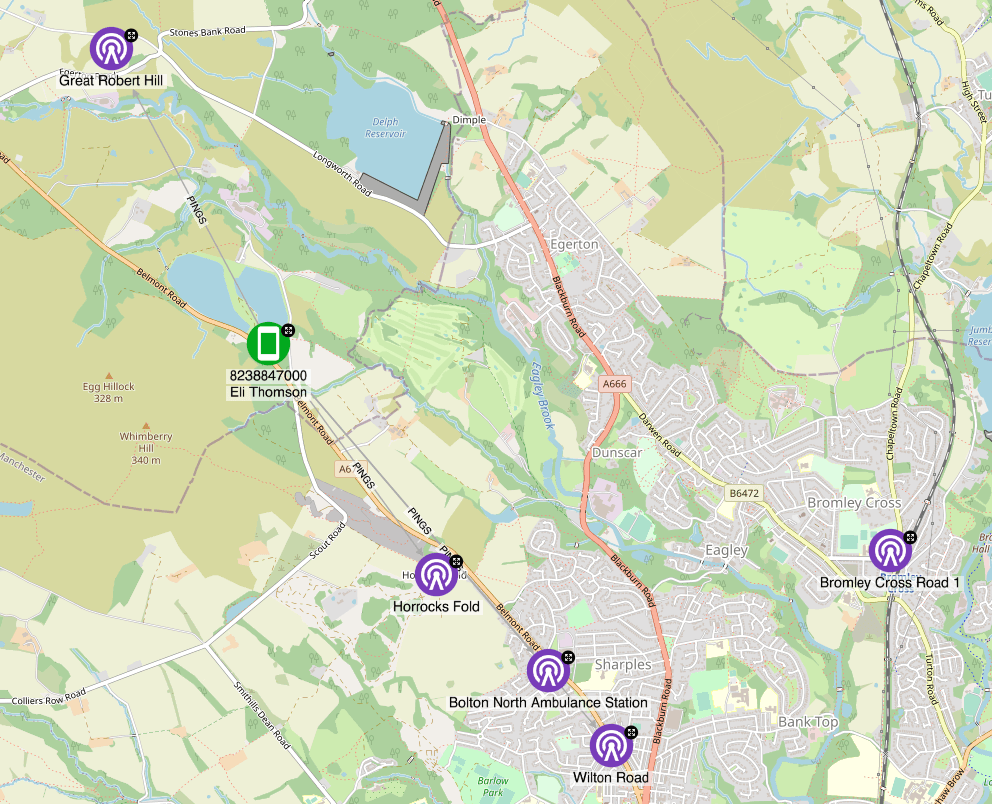
Hume’s graph-native visualisations are particularly well-suited to this kind of analysis. By representing data as nodes and relationships between those nodes as edges, analysts can easily query and visualise complex patterns and connections. They can also use advanced graph algorithms, such as community detection and centrality measures, to identify clusters of related individuals or events.
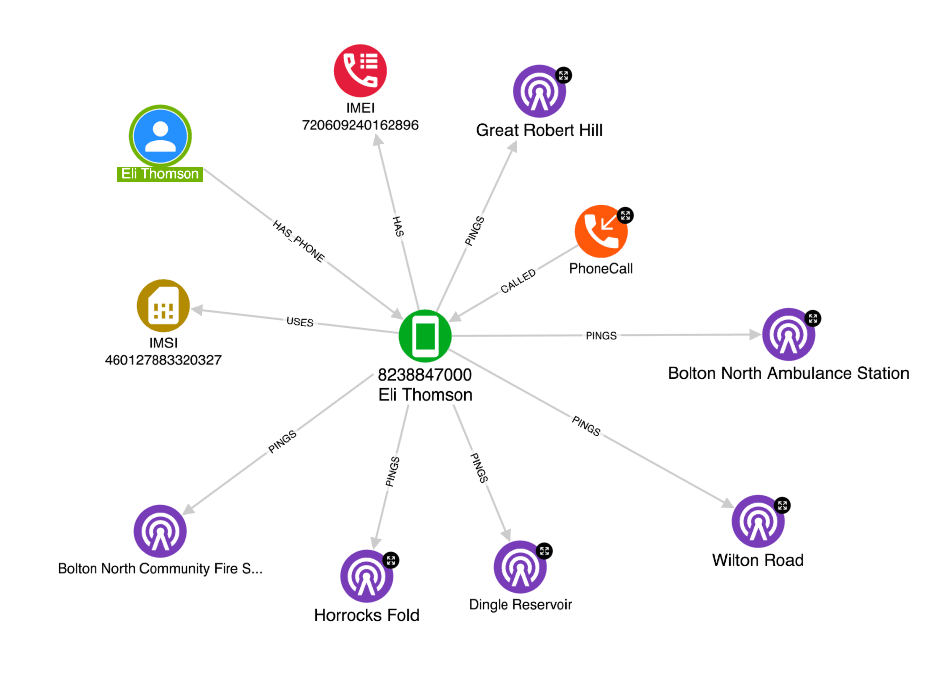
The intelligence analysis team found another advantage of using Hume for geospatial and temporal analysis is the ability to combine multiple data sources. For example, analysts were able to enrich, process and connect their CCTV footage with data collected from mobile phone towers to more accurately track the movements of the individuals of interest. By integrating this data into Hume’s single view of intelligence, analysts could easily perform queries and analyses across all of the available data sources which had been laborious and time-consuming when performed on their traditionally siloed data sets.
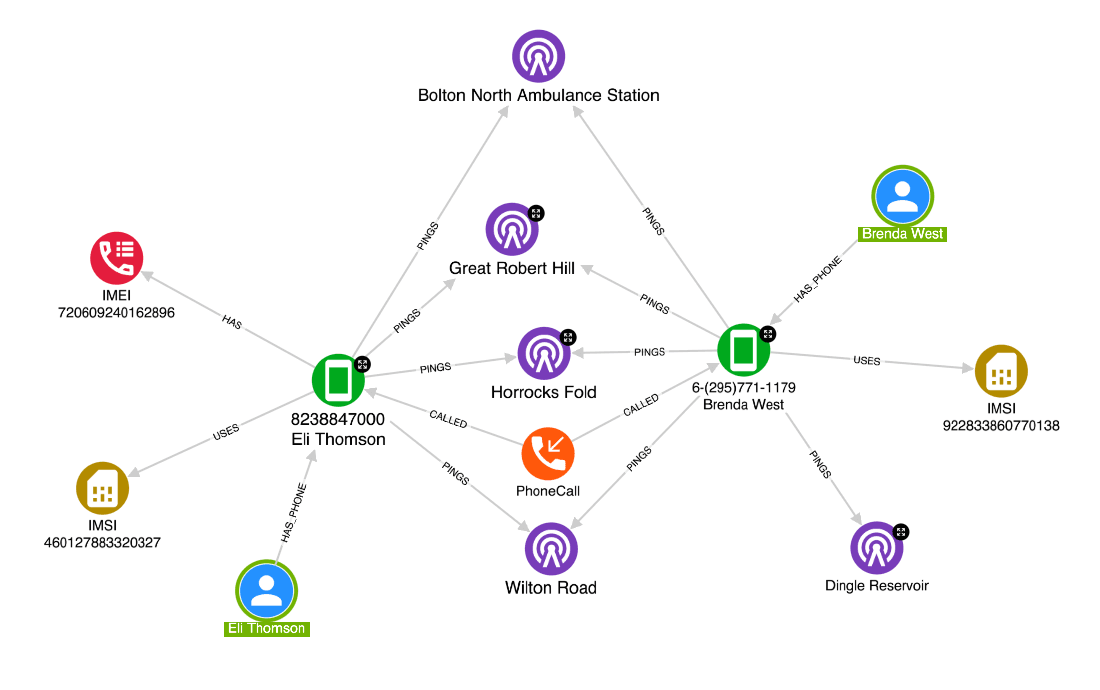
Thanks to the geospatial and temporal analysis, the intelligence team was able to enrich and connect sufficient evidence around a suspect of the burglaries. Hume was the driving force to lead and guide the police to the suspect’s phone data and CCTV footage. Finally, the team was able to build a compelling case against the perpetrator, leading to a successful conviction.
Conclusion
The utilisation of geospatial and temporal analysis in Hume has revolutionised the way crimes are solved. By combining the power of geographical and time-based data, it is now simpler to find relevant information and solve crimes more efficiently. With these powerful tools at our disposal, we can make a positive impact in our communities by solving crimes and bringing justice to the victims. Using geospatial and temporal analysis, we can easily identify patterns and trends in crime data, allowing us to make informed decisions and formulate strategies to prevent and reduce crime. Furthermore, geospatial and temporal analysis can be used to identify the locations where crimes are most likely to occur, enabling us to deploy resources more effectively.
Overall, geospatial and temporal analysis are invaluable tools for crime analysts. By leveraging these tools, we can make more accurate predictions regarding crime and devise strategies for preventing and solving crimes. Moreover, as the technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see even more powerful solutions to crime in the future.


